“The future isn’t just around the corner; it’s already here with VR, AR, and 3D reality solutions!”
Introduction
Picture this: you slip on a headset, and suddenly you’re standing on a tropical beach, feeling the warm breeze against your skin. Or, you’re in a classroom, surrounded by 3D models of planets, zooming past asteroids and moons. This isn’t science fiction—this is the magic of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and 3D reality solutions. These groundbreaking technologies are no longer just concepts for video games or sci-fi movies; they’re transforming entire industries and reshaping the way we interact with the world.
In this blog, we’re about to take a deep dive into how VR applications are revolutionizing everything from education to entertainment, business to healthcare. You’ll learn why these technologies are no longer a “nice-to-have” but a “must-have” in today’s fast-evolving digital landscape. We’ll explore the best VR applications currently pushing boundaries, and how businesses are leveraging virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D reality solutions to stay ahead of the curve.
So, whether you’re a tech enthusiast eager to stay updated, a business professional wondering how VR can boost your bottom line, or someone simply curious about the buzz, this guide has got you covered. We’ll bring you the latest insights, stats, and real-world examples to show you exactly why VR applications are the future and how they’re changing everything we thought we knew about interaction, engagement, and experience.
Let’s break down how virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D reality solutions are transforming industries—one immersive experience at a time. Ready to explore? Let’s dive in!
Why VR, AR, and 3D Reality Solutions Matter
-
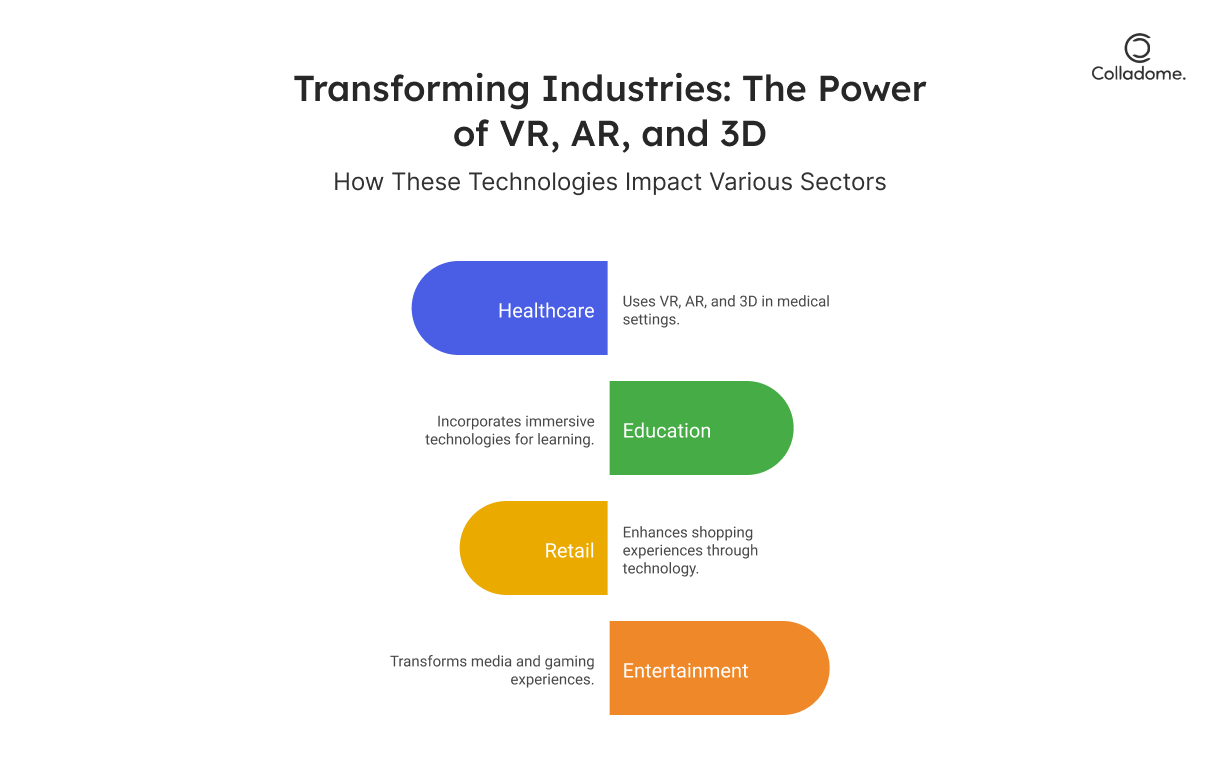
Transforming Industries
-
Healthcare:
- VR applications like surgical simulations allow doctors to practice in a risk-free virtual environment before performing real surgeries, improving precision and reducing risks.
- AR-based diagnostics overlay digital data on real-world images, assisting healthcare professionals in real-time decision-making and diagnosis.
-
Education:
- Immersive AR and VR tools create experiential learning environments, allowing students to explore historical sites, conduct science experiments, and interact with the material in a dynamic way.
- Subjects like history and science come to life, making learning interactive and engaging.
-
Retail:
- 3D reality solutions allow customers to virtually try on products, design custom spaces, or see how items fit into their homes without stepping foot in a store.
- It’s a revolution in the retail experience, enhancing customer satisfaction through personalization and convenience.
-
Entertainment:
- AR and VR are transforming entertainment by offering immersive gaming experiences and interactive cinematic adventures.
- From fully interactive video games to 360-degree movies, AR and VR are changing the way we consume entertainment.
-
-
Enhancing Efficiency
-
Virtual Reality:
- VR is streamlining business processes such as prototyping and employee training, saving companies time and money.
- By allowing businesses to virtually test products or train teams, they can make better decisions with fewer resources.
-
Augmented Reality:
- AR improves operational efficiency by overlaying real-world data with digital information in industries like logistics.
- AR can guide workers through complex tasks, helping them improve accuracy and speed.
-
-
Personalizing Experiences
-
3D Reality Solutions:
- VR and AR technologies enable highly personalized experiences, from virtual tours of homes to tailored gaming environments.
- Consumers can try products in their own homes virtually, customizing designs, or exploring new environments before making decisions.
- In gaming, VR offers users the ability to build their own virtual worlds, creating unique and engaging experiences.
-
These powerful technologies—VR, AR, and 3D reality solutions—are revolutionizing industries, enhancing efficiency, and providing more personalized experiences. Ready to embrace the future? The best VR applications and AR solutions are here to transform the way we live, work, and play!
| Industry | How It’s Getting Shaken Up | Why You Should Care |
| Healthcare | VR simulates surgeries, AR helps in real-time diagnostics. | Precision, fewer risks, and better outcomes. Trust us, your doctor will thank you. |
| Education | VR and AR bring history, science, and more to life. | Get ready to actually enjoy learning (yes, we said it)! |
| Retail | 3D tech lets you try before you buy—virtually. | Shop smarter, not harder. You can even try on clothes without changing! |
| Entertainment | VR turns gaming into an immersive experience, AR adds a twist. | Your gaming world just went 3D. Step into the action. |
| Business Efficiency | VR speeds up prototyping and AR boosts operations. | Cut the fluff, save time, and streamline your processes. It’s a no-brainer. |
| Personalized Fun | 3D solutions give you custom virtual tours and immersive gaming. | Tailored experiences that’ll make you feel like a VIP every time you use them. |
What Are VR, AR, and 3D Reality Technologies?
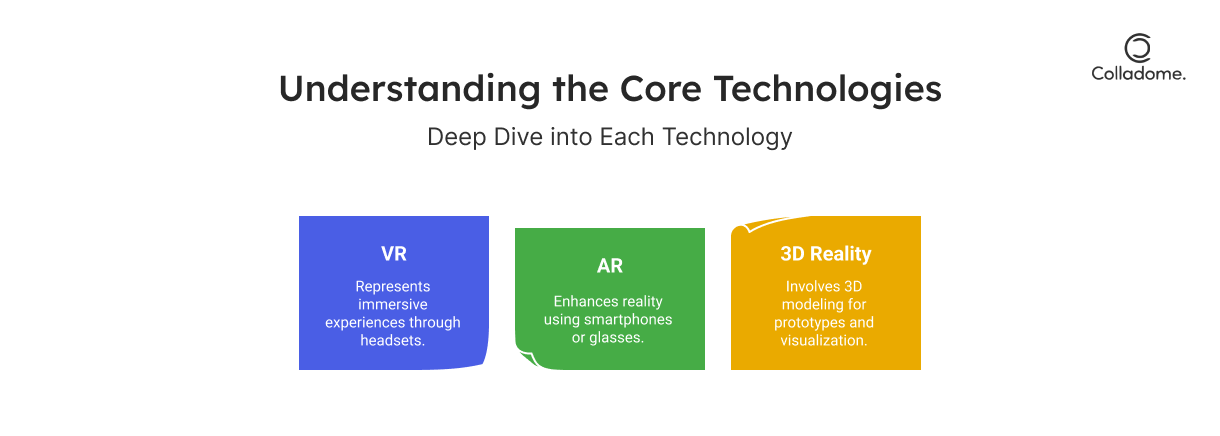
1. Virtual Reality (VR)
- Definition: Imagine stepping into an entirely new world. VR completely replaces your surroundings with a simulated environment. Think of it as a portal to a whole new dimension!
- Examples:
- Oculus Quest – Take your gaming to the next level. The virtual world becomes your playground.
- VR Training in Aviation – Forget textbooks! Trainees fly through realistic air simulations, all from the safety of the ground. It’s like being in a flight simulator without the turbulence!
2. Augmented Reality (AR)
- Definition: AR doesn’t make you leave the real world—it just enhances it by adding virtual elements. It’s like sprinkling a little bit of magic over reality.
- Examples:
- Pokemon Go – Catching Pikachu on your street? AR makes it happen, blending your world with the digital one.
- IKEA Place – Want to see how that new sofa fits in your living room? Just use your phone to superimpose the furniture in real time. No measuring tape is required!
3. 3D Reality Solutions
- Definition: 3D technology creates lifelike digital models that look and feel real. When combined with VR or AR, it’s like stepping into a 3D movie—except you’re the star.
- Examples:
- Virtual Walkthroughs in Real Estate – No need to visit every house. Walk through properties digitally before stepping foot inside.
- 3D Printing for Prototyping – Designers create physical prototypes from digital blueprints. Want to build your dream product? Just 3D print it!
How These Technologies Are Applied: From Business to Consumer
For Businesses: Power Up with VR, AR, and 3D Solutions

-
Training Employees:
Say goodbye to boring PowerPoint slides. VR offers realistic simulations for hands-on training in fields like aviation, healthcare, and manufacturing. Employees get to practice in a safe, immersive environment. Imagine teaching a surgeon how to perform complex surgeries with zero risks—hello, VR!
-
Product Demonstrations:
AR is your best friend when it comes to showcasing products. Brands can allow customers to virtually test products—whether that’s trying on clothes or placing virtual furniture in their living room. It’s like giving your clients a magic wand to play with your product before they buy.
-
Prototyping & Design:
With 3D modeling and VR, businesses can prototype designs without the costly materials. Why wait for a product to be built when you can virtually build it, tweak it, and test it all within a digital space? Quick, efficient, and cost-effective!
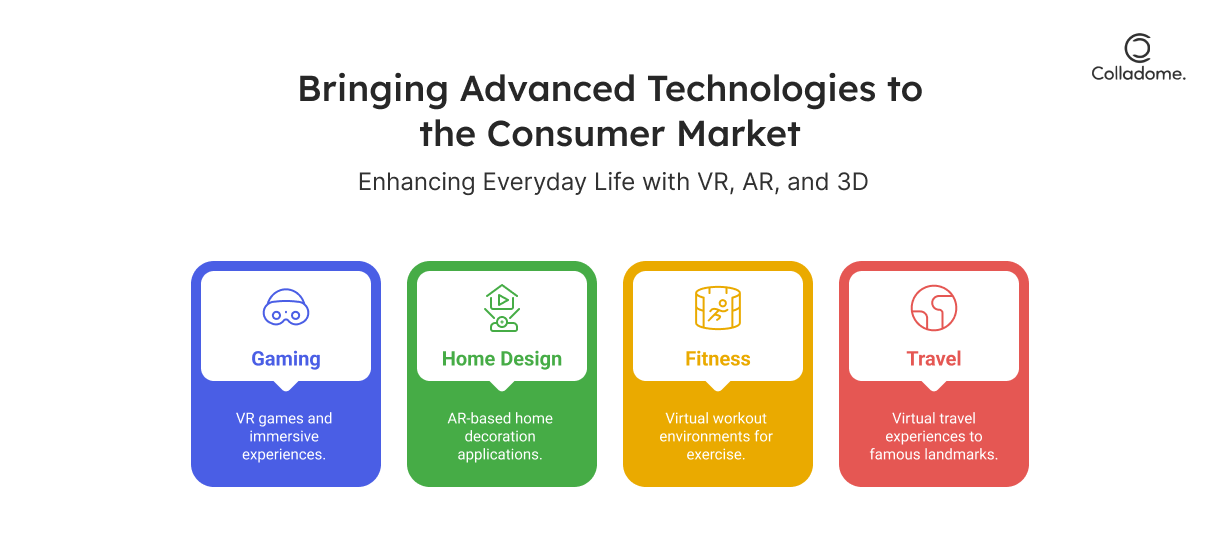
For Consumers: Enhancing Your Everyday Life
-
Gaming:
Virtual reality gaming isn’t just playing—it’s living the game. Whether you’re slaying dragons or solving mysteries, VR apps like Oculus Rift and HTC Vive throw you into the heart of the action. Ever dreamed of walking through a video game? Now you can!
-
Home Design:
Forget imagining what your couch will look like in your living room. AR apps, like IKEA Place, let you virtually place furniture in your home. You can design your perfect living space without lifting a finger. It’s like being an interior designer, but way cooler.
-
Fitness & Wellness:
VR apps are taking fitness to the next level. With apps that simulate running through the Swiss Alps or swimming with dolphins, exercise is no longer a chore—it’s an adventure. Get your fitness on while traveling the world, all from the comfort of your home.
-
Virtual Travel & Exploration:
AR and VR give consumers the ability to travel—without ever packing a suitcase. Want to visit the Louvre or take a walk on the Great Wall of China? VR lets you explore landmarks, museums, and cities in stunning detail, all from your living room couch.
Real-Time Examples
In India: The Digital Revolution is Here
-
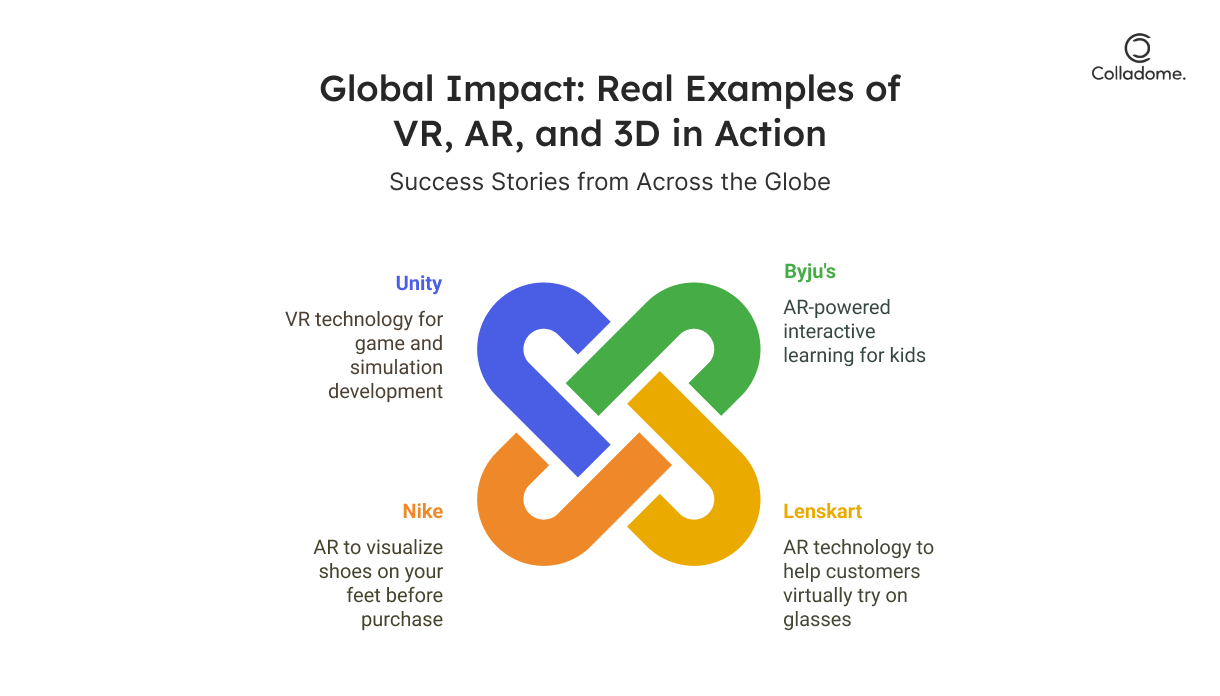
Byju’s VR Learning
- Impact: Byju’s is shaking up education like never before with VR learning modules. Gone are the days of sitting through dull textbooks and endless lectures. Now, students can dive into a world of gamified lessons, making complex topics like physics and history come to life.
- Result: A jaw-dropping 85% improvement in concept retention. With immersive VR content, students are not just learning—they’re remembering! (Source: Byju’s)
- Why It Matters: VR is making education not just fun but effective. Byju’s is proving that learning doesn’t have to be boring—it can be an adventure.
-
Lenskart’s AR Glasses Try-On
- Impact: Buying glasses has never been easier (or more fun). Lenskart is bringing augmented reality into your shopping experience with their AR Glasses Try-On feature. Just snap a picture, and voila! Try on thousands of frames right from your phone.
- Result: An impressive 30% increase in conversion rates. Customers are loving the ability to virtually “try before they buy,” making eyewear shopping hassle-free and confident. (Source: Lenskart)
- Why It Matters: AR is creating a smoother, more personalized shopping experience, proving that technology is the ultimate shopping assistant.
Worldwide: Big Players, Big Wins
-
Nike’s AR Shoe Fitting App
- Impact: Let’s face it—ordering shoes online without trying them on can be a gamble. Nike’s AR Shoe Fitting App is solving this problem by letting you “try on” shoes virtually. Simply scan your feet, and the app gives you a personalized size recommendation. Say goodbye to those painful returns.
- Result: Return rates dropped by 20%. Nike isn’t just selling shoes—they’re selling confidence. (Source: Nike)
- Why It Matters: AR is bridging the gap between online and in-store shopping, improving customer satisfaction while slashing return rates. Talk about a win-win!
-
Unity’s VR Training Simulations
- Impact: Training in high-risk industries like automotive and healthcare can be expensive and dangerous. Unity’s VR training simulations are turning this around by offering virtual environments where employees can practice skills without any real-world risks. Need to fix a car engine or perform surgery? VR’s got you covered.
- Result: Training costs dropped by 50%. Virtual reality is not just making training more engaging—it’s making it more affordable, too. (Source: Unity)
- Why It Matters: VR is not only enhancing skills but also slashing training budgets. Who knew learning could be so cost-effective and safe?
Statistics
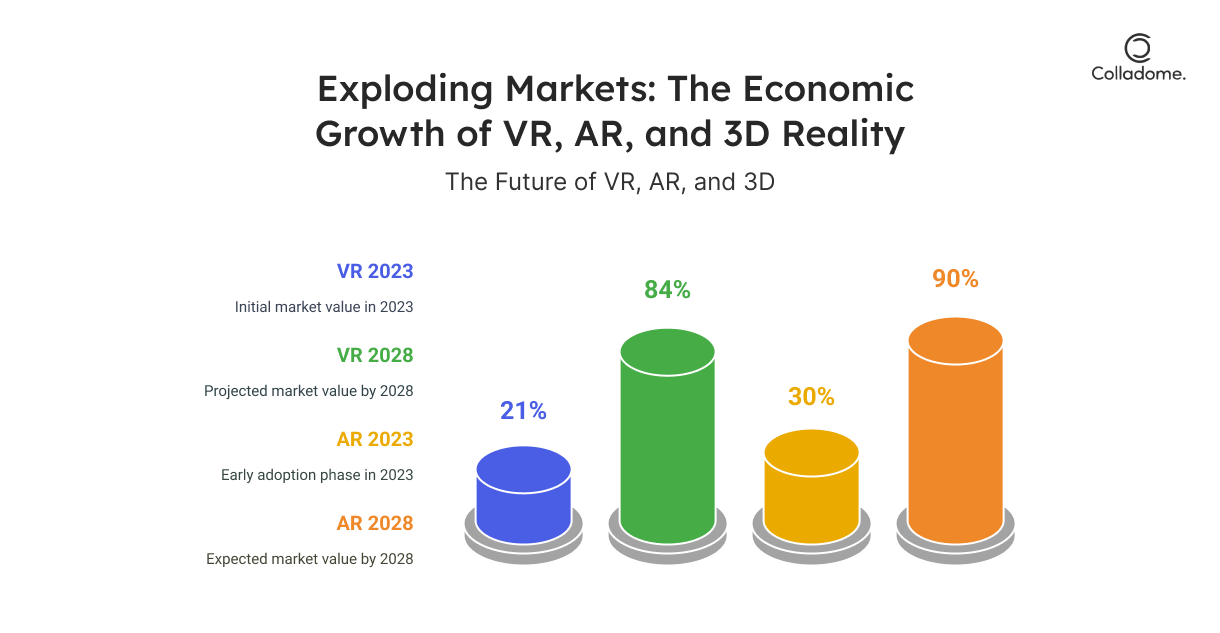
- VR Market Growth: The global VR market is projected to grow from $21 billion in 2023 to $84 billion by 2028. (source)
- AR Adoption: 70% of businesses are expected to adopt AR tools by 2025. (source)
- Customer Engagement: AR increases customer engagement by 33%. (source)
- Healthcare Training: VR reduces surgical training errors by 38%. (source)
- 3D Solutions in Real Estate: 85% of homebuyers prefer virtual tours before visiting properties. (source)
Conclusion
Virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D reality solutions aren’t just the latest trends—they’re game-changers. These technologies are revolutionizing industries, from education and healthcare to retail and entertainment, creating opportunities that were once the stuff of science fiction. We’re no longer talking about futuristic fantasies; we’re talking about real-world applications that are driving tangible results. Whether it’s enhancing customer experiences, improving training programs, or optimizing operations, VR, AR, and 3D solutions are the tools shaping the future. At Colladome, we see these technologies as a powerful force for driving innovation and efficiency. Imagine the possibilities—immersive customer journeys, data-driven decisions, and smarter processes—all powered by cutting-edge immersive tech.
Key Takeaways:
- VR, AR, and 3D solutions are transforming industries from education to retail.
- Real-world applications are delivering concrete results, including cost savings, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased engagement.
- The time to explore and embrace these technologies is now—don’t wait to unlock new opportunities.
Call to Action:
So, what are you waiting for? The future is now, and it’s calling for businesses and individuals to dive headfirst into the world of VR, AR, and 3D reality solutions. Whether you’re looking to enhance your customer experiences, streamline business operations, or revolutionize your training processes, the possibilities are limitless. At Colladome, we’re already integrating these technologies into our strategy, and we can help you do the same. So, why not take the plunge? Explore VR, AR, and 3D solutions and let us show you how they can elevate your projects to the next level. The future is immersive—don’t get left behind!









5 Responses
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/id/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/en-ZA/register-person?ref=JHQQKNKN
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.